
Properly documenting and recording dividend payments is crucial for maintaining transparency and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. Failing to accurately reflect these payments in the statement of retained earnings can result in financial mismanagement and ultimately harm the company’s reputation and credibility. Retained earnings can be used in a variety of ways, such as paying dividends to shareholders or reinvesting earnings back into the business. By looking at the example retained earnings, shareholders can get a sense of how profitable a company has been and how retained earnings can help business owners in the future.
Impact of Net Income and Dividends
Beginning and closing retained earnings are the same as the amount of retained earnings in the period 1 and period 2 of the balance sheet. Mark is an accounting and finance professional with over a decade of experience in public accounting and consulting. As both an accountant and entrepreneur, he is passionate about helping clients strategically organize and grow their businesses to reach their goals.
What Is Net Income and How Is It Calculated in Accounting?
To compute Retained Earnings Net retained earnings statement Profit from the Income Statement for the accounting period is taken. Then dividends are deducted (if any) and remaining balance is added the to the Retained Earnings balance on the Balance Sheet. Let us understand how retained income statement is useful for an organization and what it indicated about the financial health of the organization through a couple of examples.

What Is the Cost of Goods Sold and How Does It Affect Gross Profit?

By analyzing trends in Restaurant Cash Flow Management retained earnings, investors can gain insight into the company’s financial health and future prospects. If retained earnings are reported to be increasing steadily over several periods, it may indicate that the company is consistently generating profits and reinvesting in its growth. On the other hand, if retained earnings would fluctuate or decline, it could signal financial instability or poor performance. For example, if a company has negative retained earnings, it means the company has incurred losses in the past that have not been recovered through profits.

It’s the springboard for the period’s financial narrative and reflects the previous period’s endgame. For those who’ve been in the financial reporting game, this familiar number is your last performance’s curtain call, carried forward as the opening act for the new period. If this is your debut statement, then you’re starting from scratch—your opening balance is zero. Your retained earnings can thus be seen as the reserves for future strategy plays or a cushion for financial hiccups.

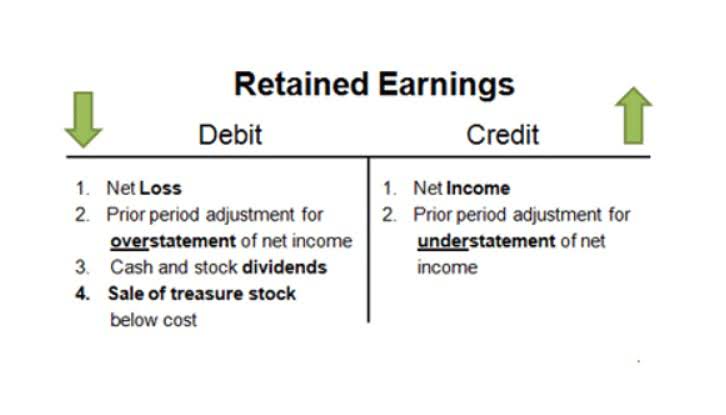
In combination, these statements reconcile performance, cash activity, and financial position into a cohesive financial picture. It’s part of shareholder’s equity and tracks how much profit the company has kept (rather than paid out as dividends). Over time, it shows the company’s accumulated profits that are reinvested in the business. Subtract any dividends paid to shareholders during this period from the retained earnings. Dividends are distributions of the company’s profits to its shareholders, decreasing the retained earnings balance. Retained earnings can be found by taking the beginning retained earnings amount, adding the net income earned during the period, and subtracting any dividends paid out to shareholders.
- This article explores the definition, importance, and components of the statement of retained earnings, as well as its role in business financial reporting.
- Also known as the Statement of Owner’s Equity, Equity Statement, or Statement of Shareholders’ Equity, this statement is created in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
- Since GAAP is so widespread, reporting according to its standards provides you ample opportunity to analyze how you stack up against similar companies.
- At the same time, those rules are not so rigid as to preclude variations in the exact structure or layout.
- When profits remain within the business, they add to the total stockholder equity.
Overlooking the Link Between Net Income and Retained Earnings
Understanding the statement of retained earnings is like comprehending the roots of a towering oak tree. Just as roots anchor the tree, absorb nutrients from the soil, and sustain its growth, retained earnings form the foundation of a company’s financial stability and future prospects. Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets. Retained earnings represent a useful link between the income statement and the balance sheet, as they are recorded under shareholders’ equity, which connects the two statements.
- One thing to keep in mind when analyzing companies is the intention behind capital allocation.
- This document reveals essential information about how a company has utilized its profits by retaining some for future investments or distributing them as dividends.
- That specific moment is the close of business on the date of the balance sheet.
- Contrary to common misconceptions, retained earnings are not a pool of cash but an expression of how much of the company’s earnings have been reinvested in the business or kept as a reserve.
- As a key indicator of a company’s financial performance over time, retained earnings are important to investors in gauging a company’s financial health.
Adding Net Income and Deducting Dividends Paid
In that case, the company may choose not to issue it as a separate form, but simply add it to the balance sheet. It’s also sometimes called bookkeeping the statement of shareholders’ equity or the statement of owner’s equity, depending on the business structure. Thanks to GAAP, there are four basic financial statements everyone must prepare . The financial statement that reflects a company’s profitability is the income statement. The statement of retained earnings – also called statement of owners equity shows the change in retained earnings between the beginning and end of a period (e.g. a month or a year). The statement of cash flows shows the cash inflows and outflows for a company over a period of time.